500 mg, MP Biomedicals
MP Biomedicals
MP Biomedicals is a worldwide corporation manufacturing and distributing systems, kits and reagents for the life science research, medical device, biopharma manufacturing and diagnostics markets. Our extensive portfolio and custom services deliver the dependability that research and industrial communities rely on to worry less and discover more. From small scale research to large scale manufacturing, MP Biomedicals has been advancing life science projects for over 50 years.
-
-
Lysozyme from Chicken Eggwhite
MP BiomedicalsLysozyme (muramidase) hydrolyzes preferentially the β-1,4 glucosidic linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine which occur in the mucopeptide cell wall structure of certain microorganisms, such as Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Extracts group specific antigens …
-
D-Glucose-6-Phosphate, Disodium Salt Hydrate
MP BiomedicalsGlucose 6-phosphate (also known as Robison ester) is glucose sugar phosphorylated on carbon 6. Very common in cells Start of two major pathways: Glycolysis and Pentose phosphate pathway Can be converted into glycogen or starch for storage D-Glucose 6-phosphate is the core…
-
4-(2-Aminoethyl)-Benzenesulfonyl Fluoride Hydrochloride
MP BiomedicalsAEBSF hydrochloride is a covalent binding serine protease inhibitor, belongs to the family of irreversible sulfonyl fluoride inhibitors that block trypsin and chymotrypsin-type enzymes. Similar in structure to the commonly used inhibitor PMSF, AEBSF offers better solubility in water, lower…
-
p-Iodonitrotetrazolium Violet
MP Biomedicalsp-Iodonitrotetazolium Violet is used as a electron acceptor for the colorimetric assay of various dehydrogenases.
-
Ribonuclease A from Bovine Pancreas
MP BiomedicalsRibonuclease belongs to pancreatic ribonuclease family. RNase A is an endoribonuclease that attacks at the 3¢ phosphate of a pyrimidine nucleotide. The sequence of pG-pG-pC-pA-pG will be cleaved to give pG-pG-pCp and A-pG. Ribonuclease A is used to remove RNA from DNA plasmid preparations…
-
Adenosine-5'-Diphosphate Monopotassium Salt Dihydrate
MP BiomedicalsAdenosine 5′-diphosphate is a P2Y receptor agonist. Adenosine 5′-diphosphate has been used to study the release, neuronal effects and removal of extracellular β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (β-NAD+) in the rat brain. Adenosine 5′-diphosphate has also been used to…
-
Apoferritin from Horse Spleen
MP BiomedicalsApoferritin is the Protein shell of ferritin. Calibration of gel filtration columns and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Acts as an anti-oxidant When added to cultured endothelial cells apoferritin is taken up in a dose-responsive manner and appears to…
-
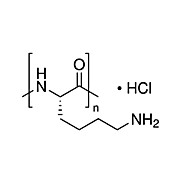
POLY-L-LYSINE HYDROCHLORIDE, 500 mg
MP BiomedicalsPoly-L-lysine is a nonspecific attachment factor for cells useful in promoting cell adhesion to solid substrates.
-
ß-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
MP Biomedicalsβ-NAD is one of the biologically active forms of nicotinic acid. Occurs in living cells, primarily in the oxidized state Coenzyme for dehydrogenases NAD usually acts as a hydrogen acceptor, forming NADH Major electron acceptor molecule in biological oxidations. Acts as a…
-
Phenazine Ethosulfate
MP BiomedicalsPhenazine ethosulfate is an intermediate which is used to detect nitric oxide reducatase activity in concert with ascorbic acid.
-
ß-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Disodium Salt
MP Biomedicalsβ-NADP is a coenzyme necessary for the alcoholic fermentation of glucose and the oxidative dehydrogenation of other substances. It occurs widely in living tissue, especially in the liver. Nicotinic acid can be converted to nicotinamide in the body and, in this form, is found as a component of…
-
Papain from Papaya Latex
MP BiomedicalsPapain is a sulfhydryl protease from Carica papaya latex. Cleaves peptide bonds of basic amino acids, leucine, or glycine Hydrolyzes esters and amides One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 µmole of N-alpha-benzoyl-L-arginine ethyl ester (BAEE) per minute at 25°C and pH 6.2 Papain…
-
Concanavalin A from Canavalia ensiformis seeds (jack beans)
MP BiomedicalsPure Canavalia ensiformis lectin (Con A) from Jackbean. Isolated by affinity chromatography on cross-linked dextran. Con A exists as a dimer below pH 5.0 and and at pH >7 it exists as a tetramer. Con-A is not a glycoprotein. The monomeric molecular weight of Con-A is 25,500. Con-A does not…
-
B-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, Oxidized Form
MP BiomedicalsThis is an ultrapure NAD, chromatographically purified to remove trace inhibitors. β-NAD, a pyridine nucleotide and biologically active form of nicotinic acid, is a coenzyme necessary for the catalytic reaction of certain enzymes. It occurs in living cells primarily in the oxidized state.…
-
Dexamethasone
MP BiomedicalsDexamethasone is an anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid that induces the production of phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein (lipocortin). It also inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase (IC50=5 nM). Dexamethasone has been shown to cause reduction in cyclin A and Cdk2 activity, inhibition of G1/S…
-
Hyaluronidase from Bovine Testes
MP BiomedicalsHyaluronidase is a glycoprotein containing 5% mannose and 2.17% glucosamine, it catalyzes the random hydrolysis of 1,4-linkages between 2-acetamido- 2-deoxy- b-D-glucose and D-glucose residues in hyaluronate. Hyaluronidase from bovine testes is a tetramer consisting of 4 equal subunits with a…
-
5-Bromo-2'-Deoxyuridine
MP Biomedicals5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine is a thymidine analog and useful for the study of DNA synthesis where it is incorporated into DNA in place of thymidine. Measure DNA synthesis Label dividing cells Study cell signaling and processes that induce cell proliferation Used as a mutagen in…
-
D-Biotin
MP BiomedicalsD-Biotin is a growth factor present in small amounts in every living cell. It is involved in naturally occurring carboxylation reactions. It occurs mainly bound to proteins or polypeptides. It is more abundant in the liver, kidney, pancreas, yeast and milk. Biotin levels are higher in cancerous…
-
Vitamin B12
MP BiomedicalsVitamin B12 (cobalamin) refers to a group of chemically-related cobalt containing molecules involved in cell processes such as DNA synthesis, fatty acid synthesis, energy production and regulation. The physiologically active forms of vitamin B12 include methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin,…
-
o-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-Galactopyranoside
MP Biomedicalso-Nitrophenyl-β-D-galactoside (ONPG) is a colorimetric substrate for b-galactosidase. This product is hydrolyzed to o-nitrophenol by the enzyme. o-Nitrophenol is yellow in alkaline solution and can be quantitated at 410-420 nm 2 . o-Nitrophenyl-β-D-galactoside is a cell culture…
-
Guanosine-5'-Triphosphate Disodium Salt
MP BiomedicalsGuanosine-5'-triphosphate, a purine nucleotide, is required as a coenzyme for protein biosynthesis in a cell-free system. Guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP), a purine trinucleotide, is a substrate for RNA polymerases and a wide range of GTPase including G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)…
-
Poly-L-Lysine Hydrobromide
MP BiomedicalsPoly-L-lysine is a positively charged amino acid polymer. Poly-lysine binds to DNA, red cell membrane and any negatively charged protein. It is typically used as a coating substrate for culture dishes, slides, etc. It enhances electrostatic interaction between negatively charged ions of the cell…
-
N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine
MP BiomedicalsN-Acetyl-D-galactosamine(GalNAc), an aminosugar, is a component of many O-linked and N-linked glycan structures. Intial O-linked sugar to many serine and threonine residues in protein glycosylations.
-
Collagenase Type II from Clostridium histolyticum
MP BiomedicalsCollagenases degrade native helical collagen fibrils. Plays an important role in connective tissue metabolism Produced by specific cells involved in repairs and remodeling processes Type II enzyme that contains greater clostripain activity Collagenase is used for collagen…
-
Collagenase Type IV from Clostridium histolyticum
MP BiomedicalsCollagenases degrade native helical collagen fibrils. It has an important role in connective tissue metabolism and is produced by specific cells involved in repairs and remodelling processes. Collagenase is used for tissue dissociation combined with other enzymes such as elastase, trypsin,…
-
RICINOLEIC ACID, 500 mg
MP BiomedicalsRicinoleic Acid is used as a substrate for the synthesis of the conjugated linoleic acids.
-
D-Biotin
MP BiomedicalsD-Biotin is a growth factor present in small amounts in every living cell. Involved in carboxylation reactions Occurs mainly bound to proteins or polypeptides Abundant in the liver, kideny, pancreas, yeast, and milk Levels are higher in cancerous tumors than in normal tissues …
-
Human Albumin, Crystallized (1X Cohn Crystallized)
MP BiomedicalsPrepared using Cohn method IV. The material is non-reactive for HbsAg, Anti-HCV 3.0, Anti-HIV-1/2 and STS (RPR). This material is also negative for HIV-1 and HCV by PCR ALBUMIN, HUMAN is recommended for use in absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) pharmacological research;…
-
Collagenase Type I from Clostridium histolyticum
MP BiomedicalsCollagenase is a protease which cleaves the triple-helical protein called collagen. There are three types of tissue collagenases, and these belong to the matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) family. Collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum has extensive use in biological studies, where it is used to…
-
Trypsin from Beef Pancreas
MP BiomedicalsTrypsin consists of a single chain polypeptide of 223 amino acid residues. Member of the serine protease family Dissolves blood clots in its microbial form Treats inflammation in its pancreatic form Trypsin cleaves peptides on the C-terminal side of lysine and arginine residues.…
-
Retinoic Acid, All Trans Isomer
MP BiomedicalsRetinoic acid (RA) is a vitamin A-derived, non-peptidic, small lipophilic molecule that mediates the functions of vitamin A required for growth and development. It affects gene transcription and modulates a wide variety of biological processes like Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, including…